Manual Network Setup Procedures
The Windows Network Setup Wizard, provided on computers running Windows XP, is a convenient way to setup your network. Sometimes though, you need to setup things manually.
In cases where you can't use the Network Setup Wizard, you'll be using the Network Connection Wizard.
- Please start by reviewing Networking Your Computers, if you haven't already.
- From Settings, open Network Connections. Find the network connection that you'll be using. The most common one is called Local Area Connection. Right click on the appropriate connection, and choose Properties. Make sure the following network components are installed, in the network items list.
- Client for Microsoft Networks.
- File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks.
- Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
- Make sure that the Internet Connection Firewall / Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) (pre-SP2), or Windows Firewall / Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) (SP2) service is running - Started and Automatic.
- Configure your firewall setup, including installing any third party firewalls, after you run the wizard.
>> Top
Local Area Connection Properties
Start from the connection items list (Start - Settings - Network Connections in Windows XP). Right click on Local Area Connection, and select Properties. This will give you the Local Area Connection Properties wizard. If you have additional or alternate network devices, your connection may have a different name.
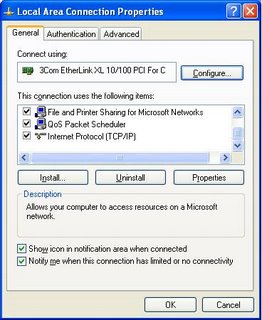
If you need to make changes to the network adapter, click on Configure. This will give you the Network Adapter Settings Wizard.
Make sure that the required protocols, for Windows Networking, are loaded. And make sure that you know what are loaded, and remove any that aren't necessary.
You'll likely be configuring TCP/IP as your primary network protocol. Double click on Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). This will open the TCP/IP Properties Wizard.
>> Top
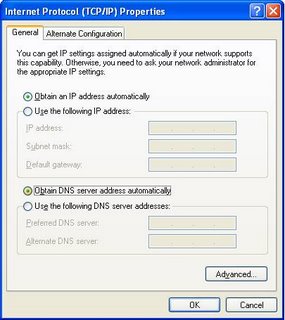
In most cases, you'll use automatic (dynamic) settings.
- Select Obtain an IP address automatically.
- Select Obtain DNS server address automatically.
- IP address
- Subnet mask
- Default gateway
- Preferred DNS server
- Alternate DNS server
>> Top
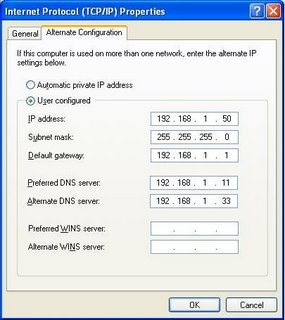
If you selected Obtain an IP address automatically, you'll have an opportunity to enter alternate settings too. If no DHCP server is available, you'll have static network settings, aka APIPA. This will let you connect with other computers on your immediate network (that are also using APIPA), and possibly other networks (with a gateway on the APIPA subnet).
>> Top
TCP/IP Properties - Advanced
Sometimes you will need to make settings beyond the basic 5 on the TCP/IP Properties window. From TCP/IP Properties, hit the Advanced button at the bottom. This opens the Advanced TCP/IP Settings wizard.
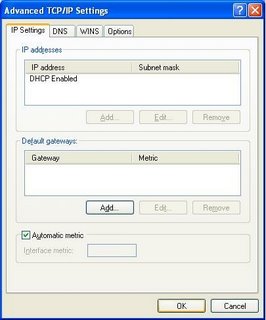
If you selected Use the following IP address, you'll be able to have your computer use multiple IP addresses.
With either automatic or manual IP addresses, you'll have a chance to specify multiple gateways. If the default gateway isn't available, your computer will try an alternate gateway, automatically.
And here, you can adjust the metric for this connection. If you have multiple network connections, and one is faster or more reliable, you can influence IP routing. These selections are reflected in the static route table. This is important with a computer with multiple network connections.
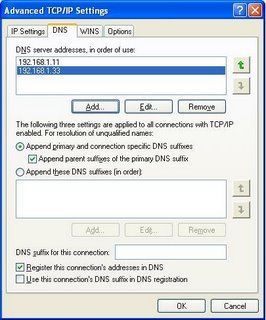
On the DNS tab, you have the ability to define more than 2 DNS servers. And additional DNS settings.
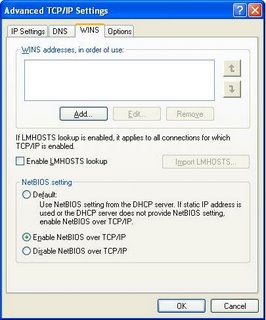
On the WINS tab, you will find the most frequently checked and set selection - the NetBIOS setting, aka NetBT.
- If your LAN has a DHCP server (not a NAT router), you can select "Default", and control the setting from a setting in the DHCP server.
- If you have a domain, and use DNS for name resolution, you can select "Disable", and use Direct Hosted SMBs.
- If you don't know what any of this means, or if you have a small LAN without a DNS server, select "Enable".
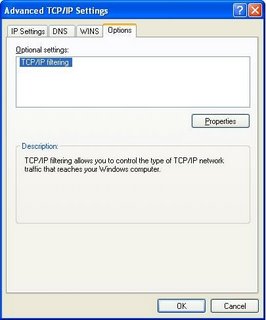
On the Options tab, you can set various TCP/IP filtering options.
>> Top






0 comments:
Post a Comment